Open RAN Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
With Open RAN’s emergence as one of the top trends in telecom, there are a lot of questions about the impact of this approach. The following are frequently asked questions we see and our answers as leaders in Open RAN.
A: The telecom industry is going through a dramatic change that can only be compared to the change that data centers went through in the 2000s; all driven by Moore’s Law. Internet of Things (IoT), digital health, e-learning, e-banking, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Industry 4.0 are just a few of the many applications which are driving mobile traffic. Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) across the globe are presented with new revenue opportunities and must scale their networks to keep up with this demand.
A: Open RAN is the movement in wireless telecommunications to disaggregate hardware and software, and to open interfaces and reduce costs. With Open RAN and the “virtualization” it brings, operators are enabled to run software-based network functions on standard commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) servers. With non-proprietary, open interfaces MNOs can use one supplier’s radios with another’s processors — something previously not possible.
A: Networks need to be agile, flexible, and easily scalable. Hardware-centric, proprietary networks are not suitable for growing network demands and changing consumption patterns. Legacy networks often pose challenges for operators to expand and scale for coverage or capacity needs and they are often difficult and costly to set up. Software at the center of the network delivers elasticity and scalability across all network components from access, to transport, and to core. A software-enabled approach provides unprecedented opportunities to bring down complexity, enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
A. The benefits of Open RAN for MNOs include a broader, best-of-breed ecosystem of hardware and software vendors which enables flexibility and increased competition, leading to lower total costs of ownership (TCO) and innovation in the telecommunications industry. For subscribers, Open RAN enables a consistent high quality user experience which exceeds performance expectations, enabling robust applications even during high peak hours and network overload.
A. There are many legacy networks deployed throughout the globe with older equipment and proprietary interfaces. Deploying, maintaining, and optimizing networks to scale for the future requires a lot of manual labor and results in high Capital Expenses (CAPEX) and Operating Expenses (OPEX). These challenges can be addressed with a software defined cloud-native architecture which is utilized in Open RAN networks.
A. The O-RAN Alliance publishes new RAN specifications, releases open software for the RAN, and supports its members with integration and testing of their implementations. The Telecom Infra Project (TIP) was formed by Facebook in 2016 as an engineering-focused, collaborative methodology for building and deploying global telecom network infrastructure, with the goal of enabling a broad ecosystem of hardware and software vendors. The Open RAN Policy Coalition represents a group of companies formed to promote policies that will advance the adoption of open and interoperable solutions.
A. “OpenRAN” typically refers to TIP Groups or could be used as a hashtag #OpenRAN. “O-RAN” with the dash refers to the O-RAN Alliance, and “Open RAN” is the overall movement to disaggregate hardware and software and to create open interfaces between them. vRAN or Virtual RAN refers to software-based network functions instead of hardware-based.
A: vRAN is a virtualized radio access network and has been a step forward in the evolution of cellular networks, helping to evolve previously hardware-driven functions by making them virtualized or software-based. However, vRAN can create vendor lock-in as it is not completely open and still contains proprietary interfaces and purpose-built hardware.
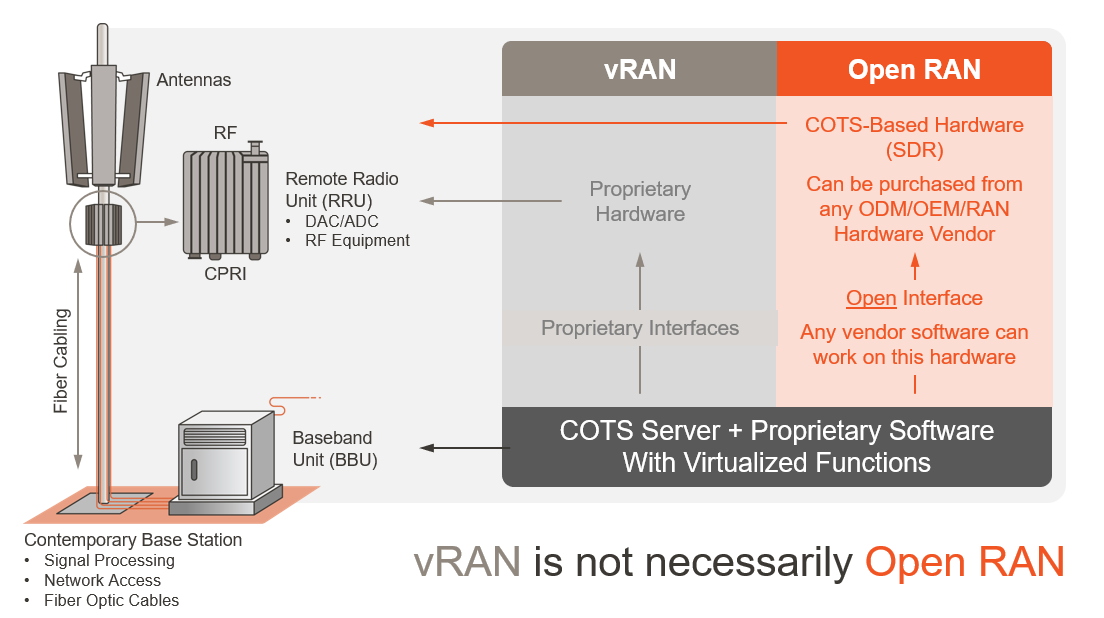
A. O-RAN architecture integrates a modular base station software stack on off-the-shelf hardware which allows baseband and radio unit components from discrete suppliers to operate seamlessly together. Open RAN disaggregates the network into the Radio Unit (RU), Distributed Unit (DU) and Centralized Unit (CU). The RU is where the radio frequency signals are transmitted, received, amplified, and digitized. The DU and CU are the computations parts of the base station, sending digital radio signals into the network. With Open RAN architecture, the interfaces or protocols between these building blocks and the software are open and non-proprietary.
A. With more hardware and software vendors in the Open RAN ecosystem, competition encourages innovation which is needed to meet the accelerated network demands of today. End-users want faster speeds and lower latency to enable state-of-the-art applications which are enabled by 5G and beyond such as autonomous driving, Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), streaming video, digital healthcare and more.
A. By complying with open and standard interfaces from organizations such as the O-RAN Alliance and implementing security testing with TIP member organizations, MNOs can ensure that their networks are interoperable and secure.
A: Two of the biggest challenges that networks face today is the cost to deploy and maintain networks due to vendor lock-in and network complexity. Open RAN can help unify different generations of access and core technologies while allowing MNOs to avoid vendor lock-in, extend their existing network investments, and make any generation (G) cellular deployments unified, simplified, and automated.
A: Most of the CAPEX required to build a wireless network is related to the RAN segment, reaching as high as 80% of the total network cost. Reductions in the RAN equipment cost will significantly help the bottom line of wireless operators as they struggle to cope with the challenges of ever-increasing mobile traffic and flat revenues. Analysts’ projections of a 5G macro-cell deployment with open architecture show pricing falling by 50% until 2022, whereas it will only fall by 30% if it is built traditionally with proprietary hardware and software. This 20% difference equates to hundreds of millions of dollars in the overall Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and will help mobile operators extend investments and become more profitable. Open RAN is the key to cost effectively deploying next-generation mobile network infrastructure.
A: It is important to emphasize that 2G & 3G networks are not going away anytime soon. Network operators in some countries are migrating off of 2G and 3G, but the majority of the world will still have a combination of 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G networks. GSMA Mobile Economy Report 2020 mentioned that 5% of the global population will still use 2G in 2025. That amounts to approximately 360 million or more users.
A: 5G is an inflection point with higher network speeds and lower latency which drives operators to re-evaluate the future of their networks. Open RAN allows MNOs to add flexibility and agility to their networks while optimizing and protecting their investments. The present-day hardware-centric, proprietary models don’t allow MNOs to scale quickly and launch new services and solutions. In contrast, software-based networks enable operators to bring down the cost of ownership while at the same time increasing the efficiency of the network. Open RAN will allow operators to modernize their networks for cost savings and prepare for the digital transformation.
Parallel Wireless Open RAN Solution
Parallel Wireless is proud to lead the charge in Open RAN innovation, supporting our customers on their network evolution journey. Deploying cloud-native, O-RAN compliant Open RAN across ALL Gs: 2G, 3G, 4G, with a broad ecosystem of partners, drives the cost down for deployments and allows MNOs to cost-effectively unleash the full potential of their networks as they migrate to 5G and beyond.