Open RAN and the Power of Automation
One of the key benefits of Open RAN is how it powers innovation, and automation is a driver of this innovation. Cloud-native automation tools such as Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD), Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP), Cloud Automation, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) enable the creation of agile, flexible, elastic, and efficient applications in modern, dynamic Open RAN environments. When automation becomes a key feature of an ALL G Open RAN solution, Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) reap the benefits of not only flexibility of choice and cost savings, but also the agility, scalability, ease of management and upgradeability that comes with the promise of a cloud-native Open RAN solution.
Challenges
MNOs are currently facing many network challenges from economics, meeting service level agreements and quality of service, to handling vendor diversity and flexibility. Open RAN networks utilizing automation will address these challenges and provide numerous benefits for MNOs.
Automation
Automated Orchestration and Management is key to benefit from a cloud-native Open RAN solution. Automation with modern tools and technologies can provide several advantages and help at different stages of network deployment, from preparation to rollout of a new network or service, then operating and monitoring the network after roll-out. Automation is also important when it comes to termination or scaling down the network.
The diagram below illustrates the four different stages of network or service deployment and the benefits of automation.
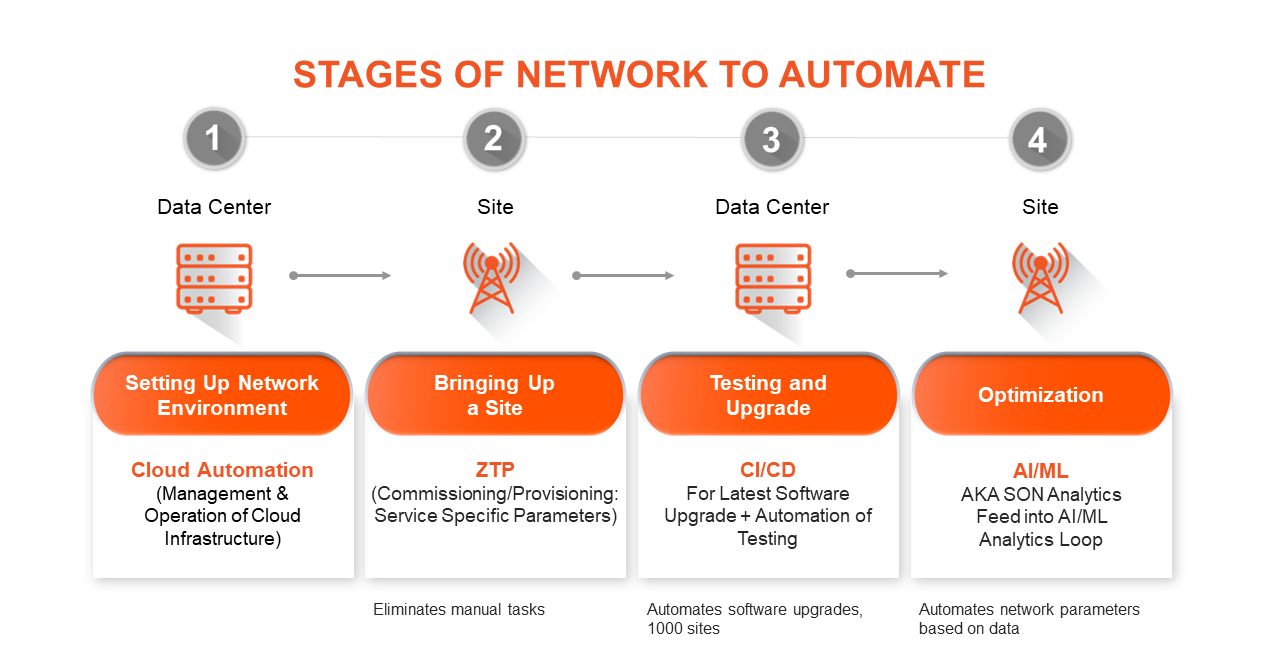
Figure 1 – Stages of Network to Automate
The following are the four stages of network automation:
Setting up the Network Environment
When setting up the network environment, cloud automation is key. It enables the management and operation of infrastructure utilizing a software-defined approach.
Advantages include:
- Automates management and operations of infrastructure
- Manages compute, storage, and networks
- Automates common repetitive tasks
- Reduces administrative overhead
- Facilitates application lifecycle management
- Significantly reduces time and effort to set up the network
- Increases resource utilization and power consumption efficiency
Bringing Up a Site
Once the infrastructure has been set up, the next step is to provision the service or bring a radio site up and running. Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) is the automated way of provisioning a service with no manual intervention needed at all.
Key advantages of ZTP are:
- Automates software installation and configuration
- Decreases complexity
- Reduces time, errors, and costs
- Relatively safe for RAN installation
- Easier to deploy a large number of sites, as no site visits are needed
Testing and Upgrade
Once the network/service has been provisioned, any new features, bug fixes or software upgrades and downgrades are done through automation utilizing Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD).
Without automation, it can become a tedious task to send people to the site for software upgrades and testing. This can be time consuming, costly and error-prone.
With CI/CD software automation, upgrades and downgrades can be done in seconds or minutes with no manual intervention. This can lead to significant reduction in costs and time.
Optimization
Once the network or service has been provisioned, it is also necessary to monitor and optimize the network to enhance and fine tune to meet the required user experience. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are key tools to providing intelligent management and operations of the network.
Networks are increasingly complex, and the only way to manage such networks is by having a self-learning and self-decision-making tool which automates the management and operations of the network.
Open RAN has natively built in an AI/ML framework into the RAN architecture with Near-RT and Non-RT RAN Intelligence Controller Functions. With the help of rApps and xApps, Open RAN integrates AI/ML-based decision-making into the solution.
ML models are trained to analyze non-RT RIC rApps based on data received from different functions in the network. The models are then used to do the inferencing and act accordingly in other RAN nodes to fine tune the network and provide the best end-user experience.
Summary
With cloud-native O-RAN compliant Open RAN networks that utilize automation tools and techniques, MNOs get an agile, flexible, efficient, elastic Open RAN solution that enables them to increase their profitability and reduce costs.
Learn more about the Parallel Wireless solution and the power of automation in Open RAN networks.
Resources: